CS#1 - Flood and wildfire risk mitigation in Greece
This page is also available in Greek.
This case study consists of a Demonstrator Site. It does not have any Follower Site.
DS#1 - "Lelantine plain, Evia island, " (Greece)

The case study in 5 minutes

Location
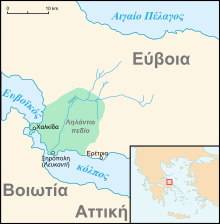
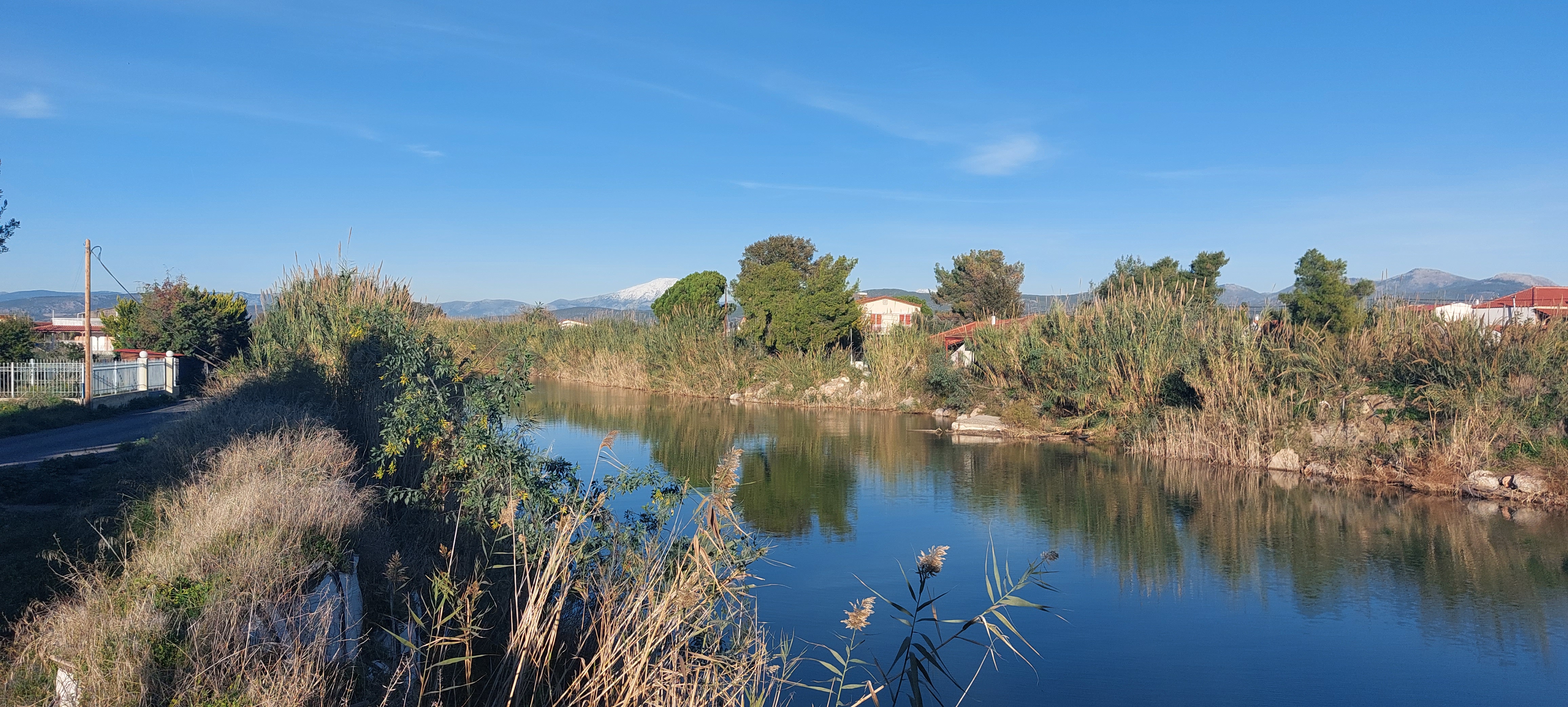
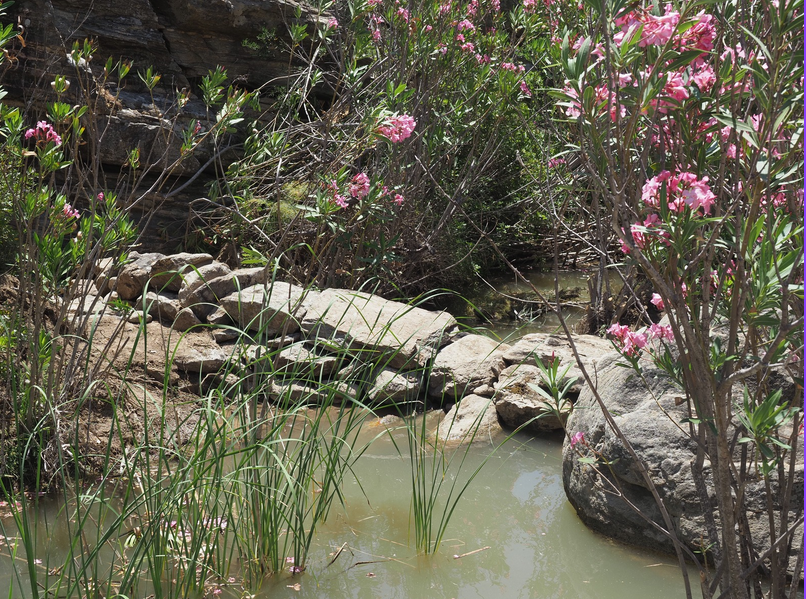
The demonstration site, the Lilas river basin, is located in the Lelantine Plain, Evia Island, Greece.

Description of the area
- Biogeographical region: Mediterranean
- Lilas river originates from Dirfys and Xerovouni mountains and flows in South Evoikos Gulf through Lelantine Plain.
- Landscape Context: Rural/agricultural area
- Evia island is the 2nd largest island in Greece
- River basin area: 273 km²
- River length: 34 km
- Tributaries length: > 170 km

Climatic Challenges


Planned activities
To date, no nature-based solutions have been implemented in the study area to mitigate the climatic challenges described above. Implemented actions have been focused on grey measures to reduce flood risk, such as gabions and dikes. Infrastructure repairs (damages to roads, bridges etc) have been conducted after major flood events.
To explore flood control measures in the study area, a minimum of 50 traditional check dams will be constructed in DS#1, in an ephemeral tributary of the Lilas river. Such check dams have been constructed for hundreds of years in the Mediterranean region, initially serving as a small-scale method to collect water for irrigation and other purposes. Here, we will explore the impact of such check dams in reducing the flood risk and in increasing water percolation, thus enriching the aquifer. Furthermore, these check dams will create small oases with the potential co-benefit of increasing biodiversity.
For fire control, NATALIE actions are prescribed burning to manage the forest fuel and the design of a fire risk management plan, which both have the potential to reduce the fire risk in the study area.
Lastly, an extended participatory approach with the local stakeholders will be undertaken to identify appropriate areas for the implementation of NBS in the future.
The Nature-Based Solutions (NBS) to be studied are:
- River Restoration
- Riparian Forest Restoration
- Floodplain Restoration and Management
- Wetland Restoration and Management
- Traditional Stone Weirs in Lilas' Tributaries (in mountainous areas)
- Forest Management

Ambition
Ambition during the project
This project is a pilot study for the implementation of NBSs in the Lelantine plain, which has suffered from major flood and fire events during the last decades. Our scope is to understand how these small-scale implementations can reduce both flood and wildfire risks in the study area, and later to design a larger-scale holistic NBS plan at the catchment area-level.
Ambition after the project
This pilot study will serve as an example for the upscaling of such NBS from the study area to the level of the catchment area. The work in WP6 on investing in ecosystem-based adaptations will have a significant role on upscaling, as it will map all the potential financial mechanisms and it will try to mature the financial conditions for implementation of similar actions in a wider scale in the area.

Questions
Ever wondered how nature can help us tackle climate change? NBS are “Solutions inspired and supported by nature, which are cost-effective, simultaneously provide environmental, social and economic benefits and help build resilience.” European Commission, 2015.
Prescribed burning is the careful and controlled use of fire under specific conditions for targeted objectives, serving as a tool in forest fuel management and forest fire prevention. This method is widely practiced around the world and is recognized as a best practice, supported by extensive research demonstrating its multiple benefits for both forest management and fire prevention.

Gallery








Involved partners







